By Michelle Shapiro and Nicki Parlitsis | Read Time: 6 Minutes
Instead of constant grazing or thinking about food all day, let’s talk about some natural ways to increase fullness and satiety!
Traditional dieting can leave us with a feeling of insatiable hunger, or maybe just a subtle dissatisfaction with what we’re eating. But that’s no way to live right?
At Michelle Shapiro Nutrition LLC, we’re all about supporting your weight loss goals from a body-neutral perspective so that you can feel like the most confident version of yourself, inside and out!
First, we’ll dig into the science behind HOW our hunger and fullness hormones even work in the first place. (We promise to keep it simple, but we won’t judge if you skip down to the bottom for the list 😊)
What is GLP-1?
One hormone that plays a significant role in satiety (fullness) is GLP-1 (glucagon-like-peptide-1).
GLP-1 is released from the small and large intestines in response to food intake. Once it’s released, it sends signals to receptors throughout the body.
Ultimately, GLP-1 works on receptors in the stomach, brain, and pancreas to helps to regulate blood sugar, improve insulin sensitivity, promote fullness and satiety, control appetite, and support weight loss.
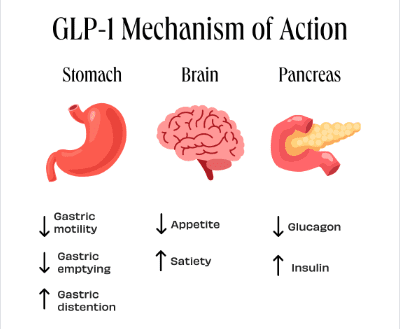
How Does GLP-1 Influence Hunger and Satiety?
GLP-1 works in several ways to increase fullness:
- It slows gastric motility and emptying in the stomach, which increases feelings of fullness.
- It increases the sensitivity of the brain to leptin, a hormone that creates a feeling of satiety. GLP-1 also inhibits the release of the hormone ghrelin, which reduces appetite and desire for food intake.
- It also promotes the growth of beta cells in the pancreas to enhance insulin secretion while also reducing glucagon secretion.
GLP-1 Agonist Medications
Current diabetic and weight loss drugs, such as Mounjaro, Wegovy, and Ozempic, have gained popularity in the media as of late. These synthetic drugs are known as GLP-1 agonists and work by mimicking the action of GLP-1 in the body (what we talked about above).
GLP-1 agonists are stronger than natural GLP-1 in the body because they are resistant to enzyme degradation, stay activated for longer, and bind more strongly to the GLP-1 receptors.
This means that GLP-1 agonist medications can result in a more dramatic and sustained glycemic control than the natural GLP-1 in the body (and why they are used in certain conditions such as diabetes).
But wait a second!!
These medications can have some pretty intense side effects:
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Diarrhea
- Stomach pain
- Fatigue
- Low blood sugar
- Muscular pain
- Inflammation of the pancreas
- Issues with the gallbladder/kidney/thyroid
- Rebound weight gain.
It’s important to note that sometimes these medications are needed for diabetes and some people may experience these side effects while others may not. We’re just giving you all of the information so you can be best informed!

8 Natural Ways to Increase Fullness Without Medication
There are many natural ways to increase GLP-1 production, which then promotes fullness, satiety, and meal satisfaction. Check them out below!
1. Eat Fermentable Fiber Foods
Focus on soluble (fermentable) fiber such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, nuts, and seeds.
Beneficial bacteria in the large intestine can ferment these fibers into short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs). These SCFAs can then bind to receptors in the intestine and pancreas to stimulate the release of GLP-1.
SCFAs can also stimulate the release of other gut hormones, such as peptide YY (PYY), which also increases fullness.
2. Have Bitter Foods
Arugula, endive, radicchio, dandelion greens, dandelion root tea, coffee, jerusalem artichoke, sesame seeds, tahini, turmeric, ginger, cacao, and rinds of citrus peels are several examples of bitter foods.
Bitter foods can enhance bile flow which in turn will support GLP-1 production.
3. Consume Pigmented Foods (Flavonoids)
Flavonoids have been found to be beneficial for blood sugar regulation given their high antioxidant properties and ability to modulate cellular signaling.
Pigmented foods such as broccoli, berries, citrus fruits, grapes, cherries, turmeric, cacao, carrots, peppers, and cabbage can lead to increased GLP-1 levels.

4. Drink Green Tea or Matcha
Green tea contains a flavonoid compound called EGCG may have a beneficial effect on GLP-1 production.
5. Include Protein at Each Meal
High protein meals can stimulate GLP-1 and promote satiety. Research suggests that whey protein, found in dairy products, may be particularly beneficial at enhancing GLP-1 levels. Eating more protein can also help to maintain muscle mass, which improves our metabolism as well!
Protein sources include chicken, beef, fish, eggs, tofu, and tempeh are great choices.
6. Add Healthy Fats to Meals
Unsaturated fatty acids are more effective at stimulating GLP-1 compared to saturated fatty acids. Unsaturated fatty acids include nuts, seeds, olive oil, fatty fish such as salmon, mackerel, black cod, and sardines.
7. Short Chain Fatty Acids (SCFAs)
SCFAs such as acetate, propionate, and butyrate can promote the secretion of GLP-1. These are available as supplements, but are also produced in the body in response to fiber intake!!
NOTE: Consult with your doctor or dietitian before starting a new supplement
8. Chew thoroughly and eat mindfully
Thoroughly chewing and slowly eating may improve GLP-1 secretion by allowing for greater nutrient digestion and absorption in the gut.
Bottom Line
There are many ways to naturally increase your satiety and fullness by stimulating GLP-1. Make sure to stock your kitchen with some of these foods and see if you start to feel more satisfied after meals!
Do you want more support in eating healthier and losing weight?
By working with one of our Registered Dietitian Nutritionists at Michelle Shapiro Nutrition LLC, you will receive personalized recommendations and one-on-one nutritional counseling to help you reach attainable goals in a way that fits your lifestyle.
We help clients to reach their weight loss goals while being body positive and improving confidence from within!